EU Sanctions On Russia: What are the top 5 questions that companies are asking? + Answers & BONUS
- Arne Mielken
- May 2, 2022
- 5 min read
There are five critical questions that any EU firm working with Russia must be able to answer. You can find them right here.
One of the biggest problems with EU sanctions is their complexity. The EU has a wide range of sanctions against Russia, and there are often confusing overlaps between them. Let's get the bottom of it, by answering questions that businesses and global trade professionals are actually asking.
Hey, BTW if you are contemplating taking over Eastern Ukraine (or more), annexing the territory to assert sovereignty, and then reintroducing the downtrodden people of Donetsk and Luhansk into Mother Russia's loving arms, you should be aware of the sanctions imposed by the European Union.
What are sanctions?
Sanctions. Wars have been fought to put a stop to them, economies have suffered as a result of depending on them, and political careers have been damaged as a result of adopting them. The EU is no stranger to sanctions: in the last 50 years, the EU has sanctioned over a hundred nations and groups of persons. As a consequence, the phrase "sanctions" may refer to a variety of government actions ranging from travel bans to asset freezes and even trade restrictions. As soon as it seems that a penalty is about to be removed or has been lifted, another one is placed without notice. It's no surprise that sanctions are a hot subject in the media and in politics...especially when it comes to dealing with Russia...
Why Sanctions Against Russia?
Since Russia's recognition of the non-government-controlled portions of Ukraine's Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts on February 21, 2022, and the unprovoked and unlawful invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, the EU has placed a slew of sanctions on Russia. They are in addition to the sanctions placed on Russia since 2014 in response to the annexation of Crimea and the failure to execute the Minsk accords.
The EU denounced the "decision of the Russian Federation to recognise as independent entities and send Russian troops to certain areas of Ukraine’s Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts" as illegal and unacceptable. According to the EU, "it violates international law, Ukraine’s territorial integrity and sovereignty, Russia’s own international commitments, and it further escalates the crisis".
Statement of the EU 24 February 2022
So far, what sanctions has the EU imposed?
From February 2022 to May 2022, the EU has issued five packages of sanctions on Russia since February, including
targeted restrictive measures (individual sanctions),
economic penalties, and
diplomatic measures.
In reaction to Belarus's role in the invasion of Ukraine, the EU imposed sanctions on the country, too. Access a full debrief on the latest in Belarus Sanctions here.
For what aim?
The goal of the economic sanctions is to
Punish Russia severely for its conduct
Effectively block Russia's ability to continue its aggression.
Target people responsible for supporting, financing or implementing actions which undermine the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine or who benefit from these actions.
What are the top 5 questions that companies are asking?
Who can I still do business with and who not? Who can I protect my business and myself?
As a business owner, what do I need to know about the trade with Russia? How are EU regulations affecting commerce with Russia, and what kind of import and export restrictions are in place?
How can I still transport goods to Russia?
Can I Still Get Paid?
What do I need to know about trading with Crimea and the "breakaway" regions?
BONUS: Other sanctions against Russia
1. Who Can I Still Do Business With and Who Not?
RPS = Restricted Party Screening is required for firms interacting with Russia in order to prevent trading with certain categories of people. As of the beginning of May 2022, the EU sanctioned 80 organisations and 1093 individuals in total, including prior individual sanctions imposed following the annexation of Crimea in 2014. Please review our detailed explainer blog entry here.
2. As a business owner, what do I need to know about the trade with Russia?
The EU has placed a number of import and export restrictions on Russia as part of the economic measures. Investigate what you can and cannot do. Because of the limitations, European firms are not permitted to sell certain items to Russia (export restrictions), and Russian entities are not permitted to sell some products to the EU (import restrictions). Please refer to our exclusive EU import and export guide for trade in goods with Russia. Read it here.
3. How Can I Still Transport Goods To Russia?
You can't simply transfer merchandise to Russia and ignore EU sanctions regulations, can you? Otherwise, a catastro-pocalypse is a distinct possibility! And if you're still confused about the new regulations and penalties, you've come to the correct spot. The EU has recently issued fresh instructions directed primarily at airlines, yachts, and road transport providers to ensure that they are aware of the dangers involved with violating the Russia/Ukraine-related sanctions regime, which, in fact, has been in effect since July 2014.
4. Can I Still Get Paid?
To restrict the funding of escalatory and aggressive activities, the EU sanctions target banks that finance the Russian military and other operations in those regions, as well as the capacity of the Russian state and government to access the EU's capital and financial markets and services. This includes a sectoral embargo on funding Russia, its government, and its Central Bank. As a result, receiving money may be more challenging than you anticipate. Here are a few things to consider before signing a contract. Read the analysis and major choices that were made.
5. What do I need to know about trading with Crimea and the "breakaway" regions?
Finding individuals responsible for the illegal and unfriendly conduct in Crimea and the two self-proclaimed republics is no easy task. As a result, the EU has amended its sanctions policy against Russia in response to their unlawful actions. So, now the EU targets commerce to and from Crimea and the two separatist regions in order to ensure that those responsible bear the economic costs of their unlawful and hostile acts. This impacts businesses which may or may not know that they trade with these regions. Read what you can and cannot do as a business owner.
Takeaway
Companies all throughout the world ask themselves the same Top 5 questions whenever there is a risk of fines. We went through the questions and gave answers to help you understand the sanctions imposed by the EU on Russia.
Overall, it is clear that foreign firms operating in Russia face significant hurdles.
And in this circumstance, it's doubtful that will change very soon. The first and most important step for any company interested in doing business with Russia is to double-check the products it produces and the marketplaces in which they are sold. If they are susceptible to these fines, customs officers who are seeking to enforce them may stop them.
Next, regardless of how these sanctions effect your company's products trade, if you conduct business in Russia, you should be on the alert for other developments involving EU sanctions laws against Russia, such as payment restrictions. Individual trade or transportation restrictions
The devil is in the details, but thanks to your Customs Manager subscription, you will always be up to date and knowledgeable. And if you have any questions, please contact us.
BONUS1 : Other Sanctions against Russia
There are a range of other sanctions imposed against Russia, too, to do with Human Rights abuses and more. Read our briefing.
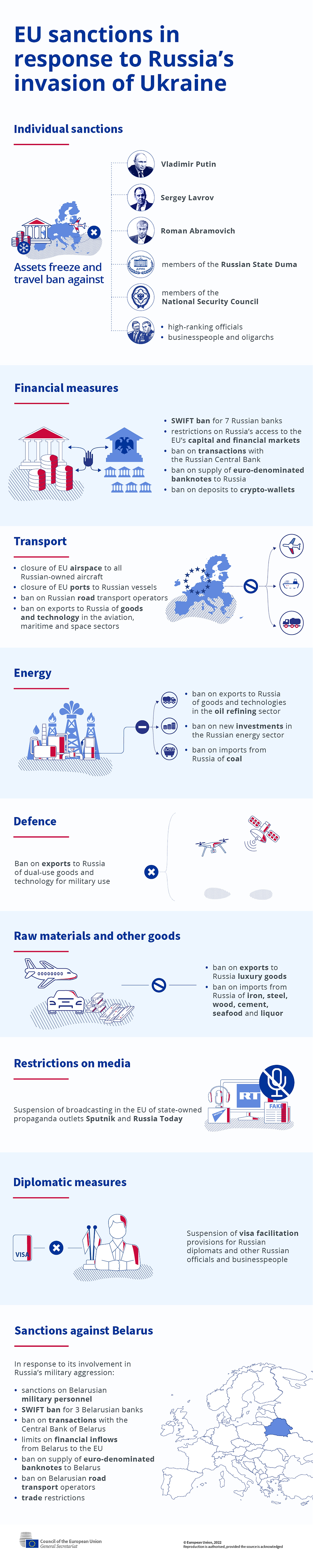
BONUS 2: In a Nutshell: Useful Infographics by the EU
The below infographics provide a very useful overview of sanctions imposed by the EU on Russia.












Comments